Appendix IV. Python Basics
本教程默认使用python3
Life is Short (You Need Python) -- Bruce Ecke (Thinking in C++)
0. python语法规范
python非常注意规范的书写语法,以缩进为例,python强制要求使用tabs/spaces来缩进。推荐使用tab或四个空格来缩进。
# use a tab
for i in range(3):
print(i)
# use 2 spaces
for i in range(3):
print(i)
# use 4 spaces
for i in range(3):
print(i)
1. Basic Practice Guide
1.0 在终端运行python脚本
创建一个python脚本welcome.py,在文件中写入如下内容:
print('welcome to python!')
在相同目录下运行:
python welcome.py #use python to run welcome.py
你也可以将python的脚本文件做成一个可执行文件,直接执行, 即在python脚本的第一行添加 python的路径:
#! /usr/bin/env python print('welcome to python!')现在就可以不需要指明python解释器,直接运行python脚本了:
chmod +x welcome.py #set the python script as executable
./welcome.py
1.1 Basic print
print("The \n makes a new line")
print("The \t is a tab")
print('I\'m going to the movies')
firstVariable = 'Hello World!'
print(firstVariable)
print(firstVariable.lower())
print(firstVariable.upper())
print(firstVariable.title())
1.2 Simple Math
print (1+1)
print (130-2.0)
print (126/3)
print (2*3)
print (2**3)
print (10%3)
1.3 if statement
| Comparison Operator | Function |
|---|---|
| < | less than |
| <= | less than or equal to |
| > | greater than |
| >= | greater than or equal to |
| == | equal |
| != | not equal |
num = 3
if num % 3 == 0:
print("if statement satisfied")
| Logical Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| and | If both the operands are True then condition becomes True. |
| or | If any of the two operands are True then condition becomes True. |
| not | Used to reverse the logical (not False becomes True, not True becomes False) |
# both the conditions are true, so the num will be printed out
num = 3
if num > 0 and num < 15:
print(num)
1.4 else and elif
my_num = 5
if my_num % 2 == 0:
print("Your number is even")
elif my_num % 2 == 0:
print("Your number is odd")
else:
print("Are you sure your number is an integer?")
1.5 Swap values
a = 1
b = 2
b, a = a, b
print(a, b)
1.6 List
请务必注意,python的索引都是从0开始的,而不是1!
| z = | [3, | 7, | 4, | 2] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
- Accessing Values in List:
# Defining a list
z = [3, 7, 4, 2]
# The first element of a list is at index 0
z[0]
# Access Last Element of List
z[-1]
- Slicing Lists:
# first index is inclusive (before the :) and last (after the :) is not.
# not including index 2
z[0:2]
# everything up to index 3
z[:3]
# index 1 to end of list
z[1:]
- Minimum, Maximum, Length, and Sum of a list:
print(min(z), max(z), len(z), sum(z))
- Add to the End of List:
x = [3, 7, 2, 11, 8, 10, 4]
y = ['Steve', 'Rachel', 'Michael', 'Adam', 'Monica', 'Jessica', 'Lester']
x.append(3)
y.append('James')
print(x)
print(y)
- list comprehension:
#Use for loops
a = []
for i in range(10):
a.append(i + 10)
print(a)
#Use list comprehension
a = [i + 10 for i in range(10)]
print(a)
1.7 Dictionary
字典是另一种可变容器模型,可存储任意类型对象。
字典的每个键值 key->value 对用冒号 : 分割,每个键值对之间用逗号 , 分割,整个字典包括在花括号 {} 中。
键一般是唯一的,如果重复最后的一个键值对会替换前面的,值不需要唯一。
- 定义和获取字典中的值:
dict = {'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'b': '3'};
dict['b']
- 修改字典:
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7, 'Class': 'First'};
dict['Age'] = 8; # update existing entry
dict['School'] = "DPS School"; # Add new entry
print ("dict['Age']: ", dict['Age'])
print ("dict['School']: ", dict['School'])
- Dict comprehension:
#Use for-loops:
a = {}
for i in range(10):
a[i] = chr(ord('A') + i)
print(a)
#Use dict comprehension:
a = {i:chr(ord('A') + i) for i in range(10)}
print(a)
2. Homework
- 在电脑上安装Anaconda,在jupyter notebook中运行本教程中的相关代码,观察输出.
3. More Reading
- Advanced Tutorial - Python - by Binbin Shi
- 廖雪峰python教程
附录:安装Anaconda和Jupyter Notebook
我们建议安装Anaconda,并使用Jupyter Notebook运行代码。读者可以下载本教程的相关文件,并运行其中的python_tutorial.ipynb文件,但是推荐初学者自己输入代码,体会python的代码风格和规范。
Anaconda
Anaconda是一个管理和安装python包的管理软件,它也包含一些非常有用的工具如jupyter notebook
- 官网下载地址,也可以在TUNA镜像站免流量下载Anaconda
| Operating System | Download Link | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Mac | Anaconda3-5.2.0-MacOSX-x86_64.pkg | |
| Linux | Anaconda3-5.2.0-Linux-x86_64.sh | 注意需要添加环境变量 |
| Windows | Anaconda3-5.2.0-Windows-x86_64.exe |
用conda安装python package,以h5py为例:
conda install h5py
用conda更新h5py至最新版本:
conda update h5py
jupyter notebook
jupyter notebook 是一款基于浏览器的交互性极强的python开发环境,在科研和工业界都广泛使用,可以帮助使用者方便的可视化结果,快速书写和调整代码,非常推荐使用。
- 打开 jupyter notebook
jupyter notebook
或者使用软件版的Anaconda中集成的jupyter软件打开。
- 使用 jupyter notebook
- 保存,增加,删除,复制,粘贴代码框,上下移动代码框,运行,终止代码框,重启kernel(将会清空内存),切换代码框版式;
- 使用shift+enter运行代码框,使用enter换行;
- 可以搭配插件nbextenstion使用,提供更多功能。
示例:
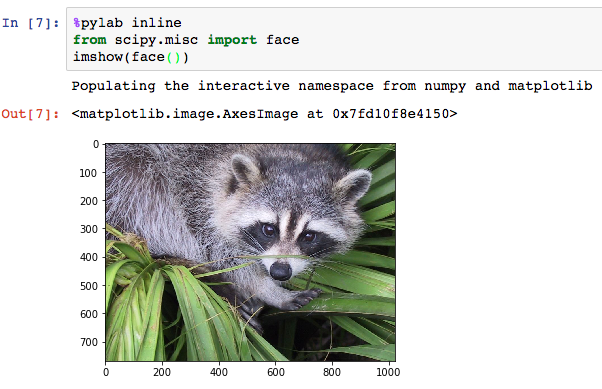
- 展示图片:
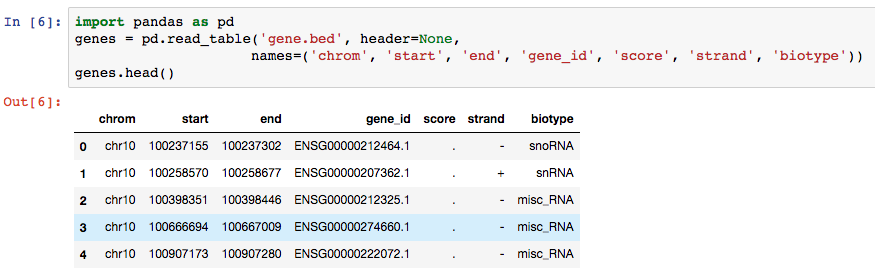
- 展示dataframe(与pandas配合):
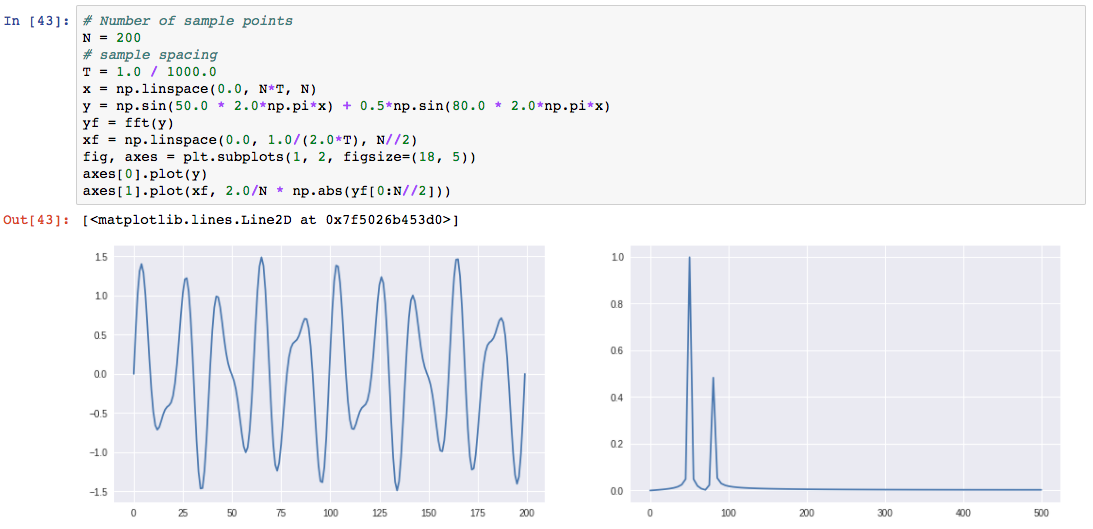
- 方便的可视化(与matplotlib,seaborn等配合):
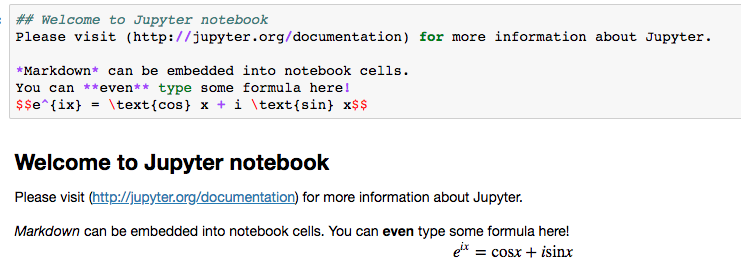
- 支持markdown: